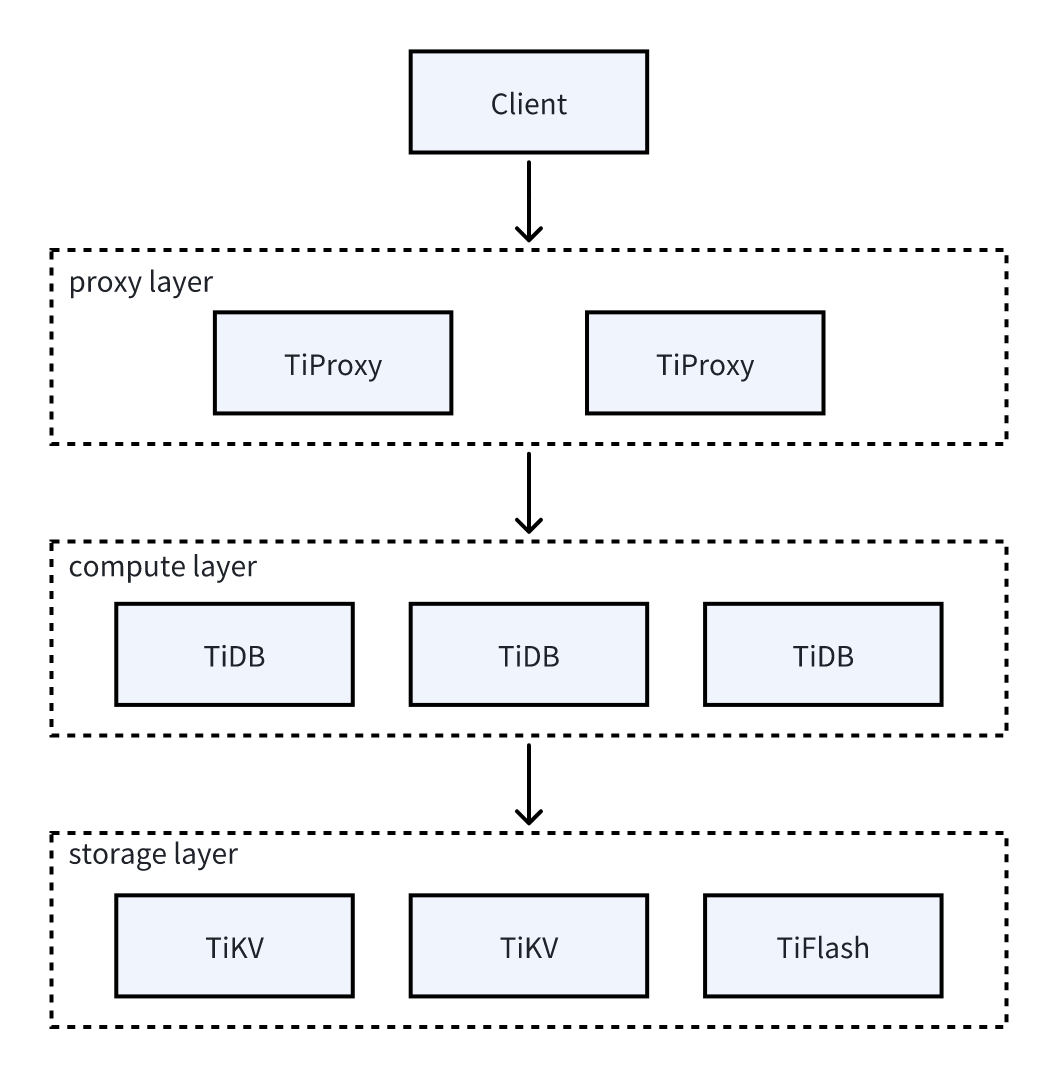
TiProxy Overview
TiProxy is the official proxy component of PingCAP. It is placed between the client and the TiDB server to provide load balancing, connection persistence, service discovery, and other features for TiDB.
TiProxy is an optional component. You can also use a third-party proxy component or connect directly to the TiDB server without using a proxy.
The following figure shows the architecture of TiProxy:
Main features
TiProxy provides connection migration, service discovery, and quick deployment.
Connection migration
TiProxy can migrate connections from one TiDB server to another without breaking the client connection.
As shown in the following figure, the client originally connects to TiDB 1 through TiProxy. After the connection migration, the client actually connects to TiDB 2. When TiDB 1 is about to be offline or the ratio of connections on TiDB 1 to connections on TiDB 2 exceeds the set threshold, the connection migration is triggered. The client is unaware of the connection migration.
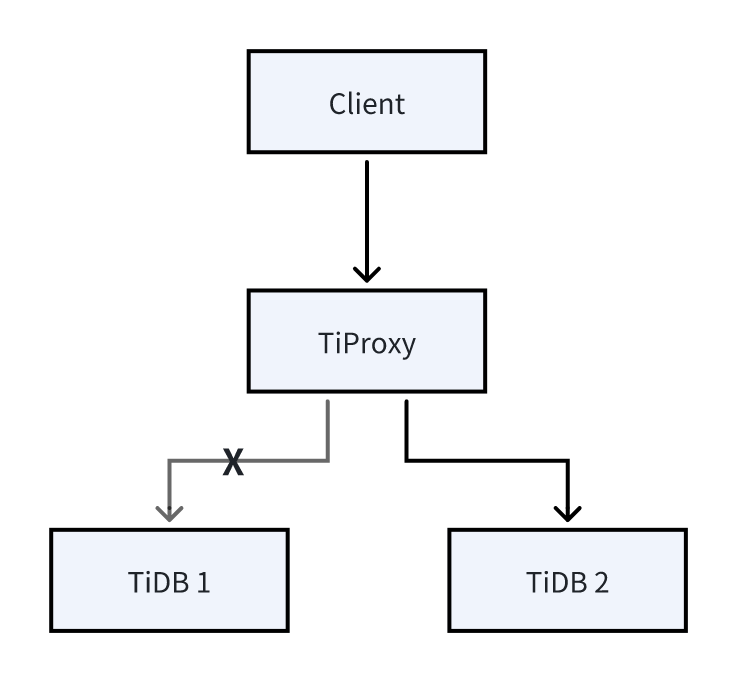
Connection migration usually occurs in the following scenarios:
- When a TiDB server performs scaling in, rolling upgrade, or rolling restart, TiProxy can migrate connections from the TiDB server that is about to be offline to other TiDB servers to keep the client connection alive.
- When a TiDB server performs scaling out, TiProxy can migrate existing connections to the new TiDB server to achieve real-time load balancing without resetting the client connection pool.
Service discovery
When a TiDB server performs scaling in or scaling out, if you use a common load balancer, you need to manually update the TiDB server list. However, TiProxy can automatically discover the TiDB server list without manual intervention.
Quick deployment
TiProxy is integrated into TiUP, TiDB Operator, TiDB Dashboard, and Grafana, which reduces the deployment, operation, and management costs.
User scenarios
TiProxy is suitable for the following scenarios:
- Connection persistence: When a TiDB server performs scaling in, rolling upgrade, or rolling restart, the client connection is broken, resulting in an error. If the client does not have an idempotent error retry mechanism, you need to manually check and fix the error, which greatly increases the labor cost. TiProxy can keep the client connection, so that the client does not report an error.
- Frequent scaling in and scaling out: The workload of an application might change periodically. To save costs, you can deploy TiDB on the cloud and automatically scale in and scale out TiDB servers according to the workload. However, scaling in might cause the client to disconnect, and scaling out might result in unbalanced load. TiProxy can keep the client connection and achieve load balancing.
TiProxy is not suitable for the following scenarios:
- Sensitive to performance: The performance of TiProxy is lower than that of HAProxy and other load balancers, so using TiProxy will reduce the QPS. For details, refer to TiProxy Performance Test Report.
- Sensitive to cost: If the TiDB cluster uses hardware load balancers, virtual IP, or the load balancer provided by Kubernetes, adding TiProxy will increase the cost. In addition, if you deploy the TiDB cluster across availability zones on the cloud, adding TiProxy will also increase the traffic cost across availability zones.
- TiDB server failover: TiProxy can keep the client connection only when the TiDB server is offline or restarted as planned. If the TiDB server is offline unexpectedly, the connection is still broken.
It is recommended that you use TiProxy for the scenarios that TiProxy is suitable for and use HAProxy or other proxies when your application is sensitive to performance.
Installation and usage
This section describes how to deploy and change TiProxy using TiUP. For how to deploy TiProxy using TiDB Operator in Kubernetes, see TiDB Operator documentation.
Deploy TiProxy
Generate a self-signed certificate.
Generate a self-signed certificate for the TiDB instance and place the certificate on all TiDB instances to ensure that all TiDB instances have the same certificate. For detailed steps, see Generate self-signed certificates.
Configure the TiDB instances.
When using TiProxy, you also need to configure the following items for the TiDB instances:
- Configure the
security.session-token-signing-certandsecurity.session-token-signing-keyof TiDB instances to the path of the certificate. Otherwise, the connection cannot be migrated. - Configure the
graceful-wait-before-shutdownof TiDB instances to a value greater than the longest transaction duration of the application. Otherwise, the client might disconnect when the TiDB server is offline. For details, see TiProxy usage limitations.
A configuration example is as follows:
server_configs: tidb: security.session-token-signing-cert: "/var/sess/cert.pem" security.session-token-signing-key: "/var/sess/key.pem" security.ssl-ca: "/var/ssl/ca.pem" security.ssl-cert: "/var/ssl/cert.pem" security.ssl-key: "/var/ssl/key.pem" graceful-wait-before-shutdown: 15- Configure the
Configure the TiProxy instances.
To ensure the high availability of TiProxy, it is recommended to deploy at least two TiProxy instances. You can use hardware load balancers to distribute traffic to each TiProxy instance, or configure virtual IP to route the traffic to the available TiProxy instance.
When selecting the model and number of TiProxy instances, consider the following factors:
- For the workload type and maximum QPS, see TiProxy Performance Test Report.
- Because the number of TiProxy instances is less than that of TiDB servers, the network bandwidth of TiProxy is more likely to become a bottleneck than that of TiDB servers. Therefore, you also need to consider the network bandwidth. For example, in AWS, the baseline network bandwidth of the same series of EC2 is not proportional to the number of CPU cores. For details, see Network performance. In such cases, when the network bandwidth becomes a bottleneck, splitting the TiProxy instance into more and smaller instances can improve QPS.
It is recommended to specify the version number of TiProxy in the topology configuration so that TiProxy will not be upgraded when you upgrade the TiDB cluster through
tiup cluster upgrade. Otherwise, the client connection might be disconnected during TiProxy upgrade.To configure TiProxy configuration items, see TiProxy configuration.
A configuration example is as follows:
component_versions: tiproxy: "v0.2.0" server_configs: tiproxy: security.server-tls.ca: "/var/ssl/ca.pem" security.server-tls.cert: "/var/ssl/cert.pem" security.server-tls.key: "/var/ssl/key.pem"Start the cluster.
To start the cluster using TiUP, see TiUP documentation.
Connect to TiProxy.
After the cluster is deployed, the cluster exposes the ports of TiDB server and TiProxy at the same time. The client should connect to the port of TiProxy instead of the port of TiDB server.
Modify TiProxy configuration
To ensure that TiProxy keeps the client connection, do not restart TiProxy unless necessary. Therefore, most of the TiProxy configuration items can be modified online. For the list of configuration items that support online change, see TiProxy configuration.
When using TiUP to change the TiProxy configuration, if the configuration item to be changed supports online change, you can use the --skip-restart option to avoid restarting TiProxy.
Upgrade TiProxy
When you deploy TiProxy, it is recommended to specify the version of TiProxy so that TiProxy will not be upgraded when you upgrade the TiDB cluster.
If you need to upgrade TiProxy, add --tiproxy-version in the upgrade command to specify the version of TiProxy:
tiup cluster upgrade <cluster-name> <version> --tiproxy-version <tiproxy-version>
Restart the TiDB cluster
When you restart the TiDB cluster using tiup cluster restart, TiDB servers are not rolling restarted, which causes the client connection to be disconnected. Therefore, avoid using this command.
Instead, when you upgrade the cluster using tiup cluster upgrade or reload the configuration using tiup cluster reload, TiDB servers are rolling restarted, so the client connection is not affected.
Compatibility with other components
- TiProxy only supports TiDB v6.5.0 and later versions.
- TiProxy's TLS connection has incompatible features with TiDB. For details, see Security.
- TiDB Dashboard and Grafana support TiProxy from v7.6.0.
- TiUP supports TiProxy from v1.14.1, and TiDB Operator supports TiProxy from v1.5.1.
- Because the interface provided by the status port of TiProxy is different from that of TiDB server, when you use TiDB Lightning to import data, the target database should be the address of TiDB server, not the address of TiProxy.
Security
TiProxy provides TLS connections. The TLS connection between the client and TiProxy is enabled according to the following rules:
- If the
security.server-tlsconfiguration of TiProxy is set to not use TLS connection, the TLS connection between the client and TiProxy is not enabled regardless of whether the client enables TLS connection. - If the
security.server-tlsconfiguration of TiProxy is set to use TLS connection, the TLS connection between the client and TiProxy is enabled only when the client enables TLS connection.
The TLS connection between TiProxy and TiDB server is enabled according to the following rules:
- If TiProxy's
security.require-backend-tlsis set totrue, TiProxy and TiDB server always enable TLS connection regardless of whether the client enables TLS connection. If TiProxy'ssecurity.sql-tlsis set to not use TLS or TiDB server does not configure TLS certificate, the client reports an error. - If TiProxy's
security.require-backend-tlsis set tofalse, TiProxy'ssecurity.sql-tlsis configured with TLS and TiDB server is configured with a TLS certificate, TiProxy and TiDB server only enable TLS connection when the client enables TLS connection. - If TiProxy's
security.require-backend-tlsis set tofalse, TiProxy'ssecurity.sql-tlsis set to not use TLS or TiDB server does not configure a TLS certificate, TiProxy and TiDB server do not enable TLS connection.
TiProxy has the following behaviors incompatible with TiDB:
- The
STATUSandSHOW STATUSstatements might return different TLS information. TheSTATUSstatement returns the TLS information between the client and TiProxy, while theSHOW STATUSstatement returns the TLS information between TiProxy and TiDB server. - TiProxy does not support certificate-based authentication. Otherwise, the client might fail to log in because the TLS certificate between the client and TiProxy is different from that between TiProxy and TiDB server, and TiDB server verifies the TLS certificate based on the TLS certificate on TiProxy.
Limitations
TiProxy cannot keep the client connection in the following scenarios:
- TiDB is offline unexpectedly. TiProxy only keeps the client connection when the TiDB server is offline or restarted as planned, and does not support failover of the TiDB server.
- TiProxy performs scaling in, upgrade, or restart. Once TiProxy is offline, the client connection is broken.
- TiDB actively disconnects the connection. For example, when a session does not send a request for a period of time longer than
wait_timeout, TiDB actively disconnects the connection, and TiProxy also disconnects the client connection.
TiProxy cannot migrate connections in the following scenarios, and thus cannot keep the client connection or achieve load balancing:
- The duration of a single statement or a single transaction exceeds the
graceful-wait-before-shutdownconfigured on the TiDB server. - The session uses the cursor to read data, and the cursor is not closed or the data is not read within the
graceful-wait-before-shutdownconfigured on the TiDB server. - The session creates a local temporary table.
- The session holds a user-level lock.
- The session holds a table lock.
- The session creates a prepared statement, and the prepared statement is invalid. For example, the table related to the prepared statement is dropped after the prepared statement is created.
- The session creates a session-level execution plan binding, and the binding is invalid. For example, the table related to the binding is dropped after the binding is created.
- After the session is created, the user used by the session is deleted or the username is changed.
Supported connectors
TiProxy requires that the connector used by the client supports authentication plugins. Otherwise, the connection might fail.
The following table lists some supported connectors:
| Language | Connector | The minimum supported version |
|---|---|---|
| Java | MySQL Connector/J | 5.1.19 |
| C | libmysqlclient | 5.5.7 |
| Go | Go SQL Driver | 1.4.0 |
| JavaScript | MySQL Connector/Node.js | 1.0.2 |
| JavaScript | mysqljs/mysql | 2.15.0 |
| JavaScript | node-mysql2 | 1.0.0-rc-6 |
| PHP | mysqlnd | 5.4 |
| Python | MySQL Connector/Python | 1.0.7 |
| Python | PyMySQL | 0.7 |
Note that some connectors call the common library to connect to the database, and these connectors are not listed in the table. You can refer to the above table for the required version of the corresponding library. For example, MySQL/Ruby uses libmysqlclient to connect to the database, so it requires that the libmysqlclient used by MySQL/Ruby is version 5.5.7 or later.