TiCDC Overview
TiCDC is a tool used to replicate incremental data from TiDB. Specifically, TiCDC pulls TiKV change logs, sorts captured data, and exports row-based incremental data to downstream databases.
Usage scenarios
TiCDC has multiple usage scenarios, including:
- Providing high availability and disaster recovery solutions for multiple TiDB clusters. TiCDC ensures eventual data consistency between primary and secondary clusters in case of a disaster.
- Replicating real-time data changes to homogeneous systems. This provides data sources for various scenarios, such as monitoring, caching, global indexing, data analysis, and primary-secondary replication between heterogeneous databases.
Major features
Key capabilities
TiCDC has the following key capabilities:
- Replicating incremental data between TiDB clusters with second-level RPO and minute-level RTO.
- Bidirectional replication between TiDB clusters, allowing the creation of a multi-active TiDB solution using TiCDC.
- Replicating incremental data from a TiDB cluster to a MySQL database or other MySQL-compatible databases with low latency.
- Replicating incremental data from a TiDB cluster to a Kafka cluster. The recommended data format includes Canal-JSON and Avro.
- Replicating incremental data from a TiDB cluster to storage services, such as Amazon S3, GCS, Azure Blob Storage, and NFS.
- Replicating tables with the ability to filter databases, tables, DMLs, and DDLs.
- High availability with no single point of failure, supporting dynamically adding and deleting TiCDC nodes.
- Cluster management through Open API, including querying task status, dynamically modifying task configuration, and creating or deleting tasks.
Replication order
For all DDL or DML statements, TiCDC outputs them at least once.
When the TiKV or TiCDC cluster encounters a failure, TiCDC might send the same DDL/DML statement repeatedly. For duplicated DDL/DML statements:
- The MySQL sink can execute DDL statements repeatedly. For DDL statements that can be executed repeatedly in the downstream, such as
TRUNCATE TABLE, the statement is executed successfully. For those that cannot be executed repeatedly, such asCREATE TABLE, the execution fails, and TiCDC ignores the error and continues with the replication process. - The Kafka sink provides different strategies for data distribution.
- You can distribute data to different Kafka partitions based on the table, primary key, or timestamp. This ensures that the updated data of a row is sent to the same partition in order.
- All these distribution strategies send
Resolved TSmessages to all topics and partitions periodically. This indicates that all messages earlier than theResolved TShave already been sent to the topics and partitions. The Kafka consumer can use theResolved TSto sort the messages received. - The Kafka sink sometimes sends duplicated messages, but these duplicated messages do not affect the constraints of
Resolved Ts. For example, if a changefeed is paused and then resumed, the Kafka sink might sendmsg1,msg2,msg3,msg2, andmsg3in order. You can filter out the duplicated messages from Kafka consumers.
- The MySQL sink can execute DDL statements repeatedly. For DDL statements that can be executed repeatedly in the downstream, such as
Replication consistency
MySQL sink
TiCDC enables the redo log to ensure eventual consistency of data replication.
TiCDC ensures that the order of single-row updates is consistent with the upstream.
TiCDC does not ensure that the downstream transactions are executed in the same order as the upstream transactions.
TiCDC architecture
TiCDC is an incremental data replication tool for TiDB, which is highly available through PD's etcd. The replication process consists of the following steps:
- Multiple TiCDC processes pull data changes from TiKV nodes.
- TiCDC sorts and merges the data changes.
- TiCDC replicates the data changes to multiple downstream systems through multiple replication tasks (changefeeds).
The architecture of TiCDC is illustrated in the following figure:
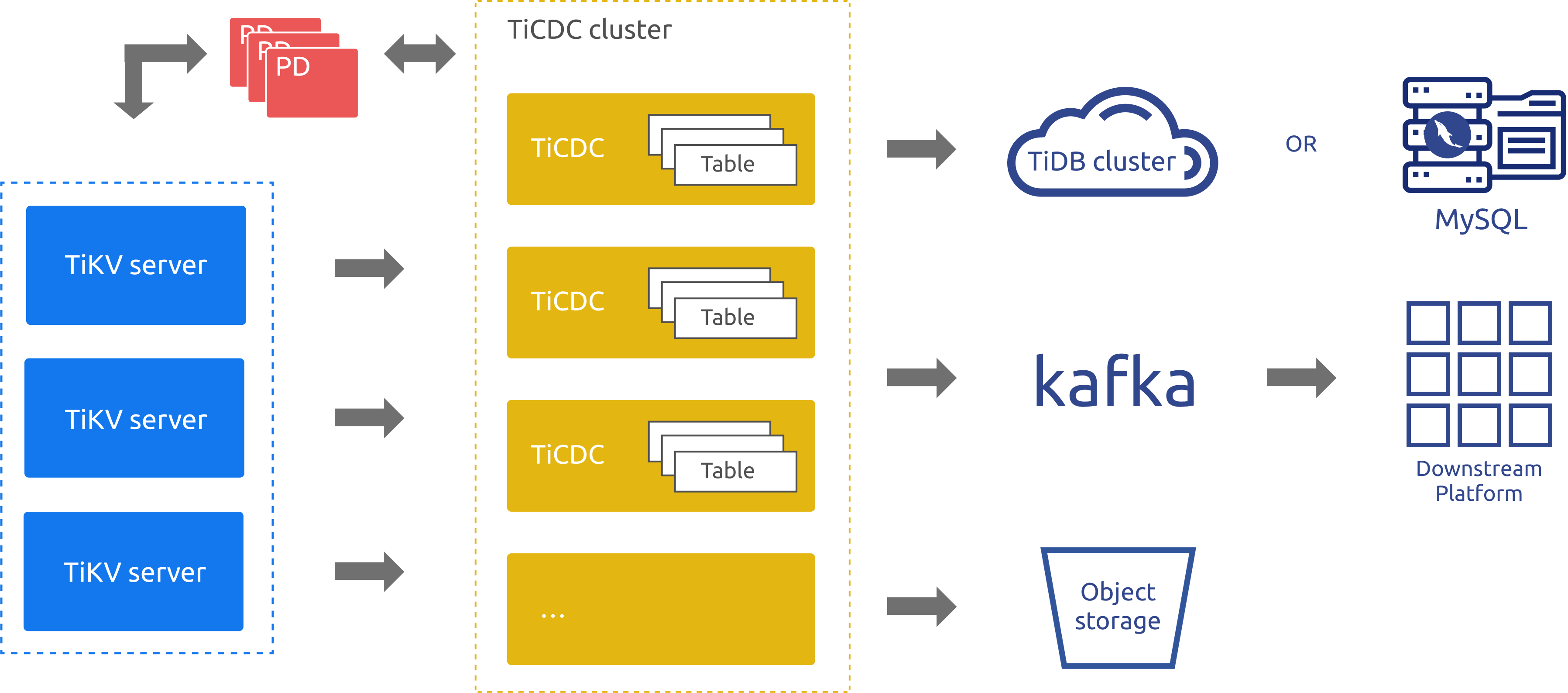
The components in the architecture diagram are described as follows:
- TiKV Server: TiKV nodes in a TiDB cluster. When data changes occur, TiKV nodes send the changes as change logs (KV change logs) to TiCDC nodes. If TiCDC nodes detect that the change logs are not continuous, they will actively request the TiKV nodes to provide change logs.
- TiCDC: TiCDC nodes where TiCDC processes run. Each node runs a TiCDC process. Each process pulls data changes from one or more tables in TiKV nodes and replicates the changes to the downstream system through the sink component.
- PD: The scheduling module in a TiDB cluster. This module is responsible for scheduling cluster data and usually consists of three PD nodes. PD provides high availability through the etcd cluster. In the etcd cluster, TiCDC stores its metadata, such as node status information and changefeed configurations.
As shown in the architecture diagram, TiCDC supports replicating data to TiDB, MySQL, Kafka, and storage services.
Best practices
If the network latency between two TiDB clusters is higher than 100 ms, it is recommended to deploy TiCDC in the region (IDC) where the downstream TiDB cluster is located when replicating data between the two clusters.
TiCDC only replicates tables that have at least one valid index. A valid index is defined as follows:
- A primary key (
PRIMARY KEY) is a valid index. - A unique index (
UNIQUE INDEX) is valid if every column of the index is explicitly defined as non-nullable (NOT NULL) and the index does not have a virtual generated column (VIRTUAL GENERATED COLUMNS).
- A primary key (
To ensure eventual consistency when using TiCDC for disaster recovery, you need to configure redo log and ensure that the storage system where the redo log is written can be read normally when a disaster occurs in the upstream.
When you replicate a wide table with a large single row (greater than 1K), it is recommended to configure the
per-table-memory-quotaso thatper-table-memory-quota=ticdcTotalMemory/(tableCount* 2).ticdcTotalMemoryis the memory of a TiCDC node, andtableCountis the number of target tables that a TiCDC node replicates.
Unsupported scenarios
Currently, the following scenarios are not supported:
- A TiKV cluster that uses RawKV alone.
- The
CREATE SEQUENCEDDL operation and theSEQUENCEfunction in TiDB. When the upstream TiDB usesSEQUENCE, TiCDC ignoresSEQUENCEDDL operations/functions performed upstream. However, DML operations usingSEQUENCEfunctions can be correctly replicated.
TiCDC only partially supports scenarios involving large transactions in the upstream. For details, refer to the TiCDC FAQ, where you can find details on whether TiCDC supports replicating large transactions and any associated risks.