Introduction to Statistics
TiDB uses statistics to decide which index to choose. The tidb_analyze_version variable controls the statistics collected by TiDB. Currently, two versions of statistics are supported: tidb_analyze_version = 1 and tidb_analyze_version = 2.
- For TiDB Self-Hosted, the default value of this variable is
1before v5.1.0. In v5.3.0 and later versions, the default value of this variable is2. If your cluster is upgraded from a version earlier than v5.3.0 to v5.3.0 or later, the default value oftidb_analyze_versiondoes not change. - For TiDB Cloud, the default value of this variable is
1.
These two versions include different information in TiDB:
| Information | Version 1 | Version 2 |
|---|---|---|
| The total number of rows in the table | √ | √ |
| Column Count-Min Sketch | √ | × |
| Index Count-Min Sketch | √ | × |
| Column Top-N | √ | √ (Maintenance methods and precision are improved) |
| Index Top-N | √ (Insufficient maintenance precision might cause inaccuracy) | √ (Maintenance methods and precision are improved) |
| Column histogram | √ | √ (The histogram does not include Top-N values.) |
| Index histogram | √ | √ (The histogram buckets record the number of different values in each bucket, and the histogram does not include Top-N values.) |
The number of NULLs in the column | √ | √ |
The number of NULLs in the index | √ | √ |
| The average length of columns | √ | √ |
| The average length of indexes | √ | √ |
Compared to Version 1, Version 2 statistics avoids the potential inaccuracy caused by hash collision when the data volume is huge. It also maintains the estimate precision in most scenarios.
This document briefly introduces the histogram, Count-Min Sketch, and Top-N, and details the collection and maintenance of statistics.
Histogram
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of data. It divides the entire range of values into a series of buckets, and uses simple data to describe each bucket, such as the number of values falling in the bucket. In TiDB, an equal-depth histogram is created for the specific columns of each table. The equal-depth histogram can be used to estimate the interval query.
Here "equal-depth" means that the number of values falling into each bucket is as equal as possible. For example, for a given set {1.6, 1.9, 1.9, 2.0, 2.4, 2.6, 2.7, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5}, you want to generate 4 buckets. The equal-depth histogram is as follows. It contains four buckets [1.6, 1.9], [2.0, 2.6], [2.7, 2.8], [2.9, 3.5]. The bucket depth is 3.
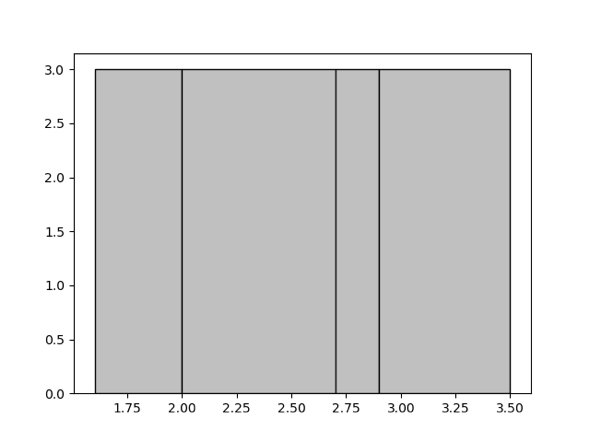
For details about the parameter that determines the upper limit to the number of histogram buckets, refer to Manual Collection. When the number of buckets is larger, the accuracy of the histogram is higher; however, higher accuracy is at the cost of the usage of memory resources. You can adjust this number appropriately according to the actual scenario.
Count-Min Sketch
Count-Min Sketch is a hash structure. When an equivalence query contains a = 1 or IN query (for example, a in (1, 2, 3)), TiDB uses this data structure for estimation.
A hash collision might occur since Count-Min Sketch is a hash structure. In the EXPLAIN statement, if the estimate of the equivalent query deviates greatly from the actual value, it can be considered that a larger value and a smaller value have been hashed together. In this case, you can take one of the following ways to avoid the hash collision:
- Modify the
WITH NUM TOPNparameter. TiDB stores the high-frequency (top x) data separately, with the other data stored in Count-Min Sketch. Therefore, to prevent a larger value and a smaller value from being hashed together, you can increase the value ofWITH NUM TOPN. In TiDB, its default value is 20. The maximum value is 1024. For more information about this parameter, see Full Collection. - Modify two parameters
WITH NUM CMSKETCH DEPTHandWITH NUM CMSKETCH WIDTH. Both affect the number of hash buckets and the collision probability. You can increase the values of the two parameters appropriately according to the actual scenario to reduce the probability of hash collision, but at the cost of higher memory usage of statistics. In TiDB, the default value ofWITH NUM CMSKETCH DEPTHis 5, and the default value ofWITH NUM CMSKETCH WIDTHis 2048. For more information about the two parameters, see Full Collection.
Top-N values
Top-N values are values with the top N occurrences in a column or index. TiDB records the values and occurrences of Top-N values.
Collect statistics
Manual collection
You can run the ANALYZE statement to collect statistics.
Full collection
You can perform full collection using the following syntax.
- To collect statistics of all the tables in
TableNameList:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableNameList [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
WITH NUM BUCKETSspecifies the maximum number of buckets in the generated histogram.WITH NUM TOPNspecifies the maximum number of the generatedTOPNs.WITH NUM CMSKETCH DEPTHspecifies the depth of the CM Sketch.WITH NUM CMSKETCH WIDTHspecifies the width of the CM Sketch.WITH NUM SAMPLESspecifies the number of samples.WITH FLOAT_NUM SAMPLERATEspecifies the sampling rate.
WITH NUM SAMPLES and WITH FLOAT_NUM SAMPLERATE correspond to two different algorithms of collecting samples.
WITH NUM SAMPLESspecifies the size of the sampling set, which is implemented in the reservoir sampling method in TiDB. When a table is large, it is not recommended to use this method to collect statistics. Because the intermediate result set of the reservoir sampling contains redundant results, it causes additional pressure on resources such as memory.WITH FLOAT_NUM SAMPLERATEis a sampling method introduced in v5.3.0. With the value range(0, 1], this parameter specifies the sampling rate. It is implemented in the way of Bernoulli sampling in TiDB, which is more suitable for sampling larger tables and performs better in collection efficiency and resource usage.
Before v5.3.0, TiDB uses the reservoir sampling method to collect statistics. Since v5.3.0, the TiDB Version 2 statistics uses the Bernoulli sampling method to collect statistics by default. To re-use the reservoir sampling method, you can use the WITH NUM SAMPLES statement.
The current sampling rate is calculated based on an adaptive algorithm. When you can observe the number of rows in a table using SHOW STATS_META, you can use this number of rows to calculate the sampling rate corresponding to 100,000 rows. If you cannot observe this number, you can use the TABLE_KEYS column in the TABLE_STORAGE_STATS table as another reference to calculate the sampling rate.
Collect statistics on some columns
In most cases, when executing SQL statements, the optimizer only uses statistics on some columns (such as columns in the WHERE, JOIN, ORDER BY, and GROUP BY statements). These columns are called PREDICATE COLUMNS.
If a table has many columns, collecting statistics on all the columns can cause a large overhead. To reduce the overhead, you can collect statistics on only specific columns or PREDICATE COLUMNS to be used by the optimizer.
- To collect statistics on specific columns, use the following syntax:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableName COLUMNS ColumnNameList [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
In the syntax, `ColumnNameList` specifies the name list of the target columns. If you need to specify more than one column, use comma `,` to separate the column names. For example, `ANALYZE table t columns a, b`. Besides collecting statistics on the specific columns in a specific table, this syntax collects statistics on the indexed columns and all indexes in that table at the same time.
> **Note:**
>
> The syntax above is a full collection. For example, after collecting statistics on columns `a` and `b` using this syntax, if you also want to collect statistics on column `c`, you need to specify all three columns using `ANALYZE table t columns a, b, c`, rather than only specifying the additional column `c` using `ANALYZE TABLE t COLUMNS c`.
To collect statistics on
PREDICATE COLUMNS, do the following:Set the value of the
tidb_enable_column_trackingsystem variable toONto enable TiDB to collectPREDICATE COLUMNS.After the setting, TiDB writes the
PREDICATE COLUMNSinformation to themysql.column_stats_usagesystem table every 100 *stats-lease.After the query pattern of your business is relatively stable, collect statistics on
PREDICATE COLUMNSby using the following syntax:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableName PREDICATE COLUMNS [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
Besides collecting statistics on `PREDICATE COLUMNS` in a specific table, this syntax collects statistics on indexed columns and all indexes in that table at the same time.
> **Note:**
>
> - If the `mysql.column_stats_usage` system table does not contain any `PREDICATE COLUMNS` record for that table, the preceding syntax collects statistics on all columns and all indexes in that table.
> - After using this syntax to collect statistics, when executing a new type of SQL query, the optimizer might temporarily use the old or pseudo column statistics for this time, and TiDB will collect the statistics on the used columns from the next time.
- To collect statistics on all columns and indexes, use the following syntax:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableName ALL COLUMNS [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
If you want to persist the column configuration in the ANALYZE statement (including COLUMNS ColumnNameList, PREDICATE COLUMNS, and ALL COLUMNS), set the value of the tidb_persist_analyze_options system variable to ON to enable the ANALYZE configuration persistence feature. After enabling the ANALYZE configuration persistence feature:
- When TiDB collects statistics automatically or when you manually collect statistics by executing the
ANALYZEstatement without specifying the column configuration, TiDB continues using the previously persisted configuration for statistics collection. - When you manually execute the
ANALYZEstatement multiple times with column configuration specified, TiDB overwrites the previously recorded persistent configuration using the new configuration specified by the latestANALYZEstatement.
To locate PREDICATE COLUMNS and columns on which statistics have been collected, use the following syntax:
SHOW COLUMN_STATS_USAGE [ShowLikeOrWhere];
The SHOW COLUMN_STATS_USAGE statement returns the following 6 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
Db_name | The database name |
Table_name | The table name |
Partition_name | The partition name |
Column_name | The column name |
Last_used_at | The last time when the column statistics were used in the query optimization |
Last_analyzed_at | The last time when the column statistics were collected |
In the following example, after executing ANALYZE TABLE t PREDICATE COLUMNS;, TiDB collects statistics on columns b, c, and d, where column b is a PREDICATE COLUMN and columns c and d are index columns.
SET GLOBAL tidb_enable_column_tracking = ON;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
CREATE TABLE t (a INT, b INT, c INT, d INT, INDEX idx_c_d(c, d));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
-- The optimizer uses the statistics on column b in this query.
SELECT * FROM t WHERE b > 1;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
-- After waiting for a period of time (100 * stats-lease), TiDB writes the collected `PREDICATE COLUMNS` to mysql.column_stats_usage.
-- Specify `last_used_at IS NOT NULL` to show the `PREDICATE COLUMNS` collected by TiDB.
SHOW COLUMN_STATS_USAGE WHERE db_name = 'test' AND table_name = 't' AND last_used_at IS NOT NULL;
+---------+------------+----------------+-------------+---------------------+------------------+
| Db_name | Table_name | Partition_name | Column_name | Last_used_at | Last_analyzed_at |
+---------+------------+----------------+-------------+---------------------+------------------+
| test | t | | b | 2022-01-05 17:21:33 | NULL |
+---------+------------+----------------+-------------+---------------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ANALYZE TABLE t PREDICATE COLUMNS;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.03 sec)
-- Specify `last_analyzed_at IS NOT NULL` to show the columns for which statistics have been collected.
SHOW COLUMN_STATS_USAGE WHERE db_name = 'test' AND table_name = 't' AND last_analyzed_at IS NOT NULL;
+---------+------------+----------------+-------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| Db_name | Table_name | Partition_name | Column_name | Last_used_at | Last_analyzed_at |
+---------+------------+----------------+-------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| test | t | | b | 2022-01-05 17:21:33 | 2022-01-05 17:23:06 |
| test | t | | c | NULL | 2022-01-05 17:23:06 |
| test | t | | d | NULL | 2022-01-05 17:23:06 |
+---------+------------+----------------+-------------+---------------------+---------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Collect statistics on indexes
To collect statistics on all indexes in IndexNameList in TableName, use the following syntax:
ANALYZE TABLE TableName INDEX [IndexNameList] [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
When IndexNameList is empty, this syntax collects statistics on all indexes in TableName.
Collect statistics on partitions
- To collect statistics on all partitions in
PartitionNameListinTableName, use the following syntax:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableName PARTITION PartitionNameList [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
- To collect index statistics on all partitions in
PartitionNameListinTableName, use the following syntax:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableName PARTITION PartitionNameList INDEX [IndexNameList] [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
If you only need to collect statistics on some columns of some partitions in a table, use the following syntax:
```sql
ANALYZE TABLE TableName PARTITION PartitionNameList [COLUMNS ColumnNameList|PREDICATE COLUMNS|ALL COLUMNS] [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
Collect statistics of partitioned tables in dynamic pruning mode
When accessing partitioned tables in dynamic pruning mode, TiDB collects table-level statistics, which is called GlobalStats. Currently, GlobalStats is aggregated from statistics of all partitions. In dynamic pruning mode, a statistics update of any partitioned table can trigger the GlobalStats to be updated.
Incremental collection
To improve the speed of analysis after full collection, incremental collection could be used to analyze the newly added sections in monotonically non-decreasing columns such as time columns.
You can perform incremental collection using the following syntax.
- To incrementally collect statistics on index columns in all
IndexNameListsinTableName:
```sql
ANALYZE INCREMENTAL TABLE TableName INDEX [IndexNameList] [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
- To incrementally collect statistics on index columns for partitions in all
PartitionNameListsinTableName:
```sql
ANALYZE INCREMENTAL TABLE TableName PARTITION PartitionNameList INDEX [IndexNameList] [WITH NUM BUCKETS|TOPN|CMSKETCH DEPTH|CMSKETCH WIDTH]|[WITH NUM SAMPLES|WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE];
```
Automatic update
For the INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE statements, TiDB automatically updates the number of rows and updated rows. TiDB persists this information regularly and the update cycle is 20 * stats-lease. The default value of stats-lease is 3s. If you specify the value as 0, it does not update automatically.
Three system variables related to automatic update of statistics are as follows:
| System Variable | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
tidb_auto_analyze_ratio | 0.5 | The threshold value of automatic update |
tidb_auto_analyze_start_time | 00:00 +0000 | The start time in a day when TiDB can perform automatic update |
tidb_auto_analyze_end_time | 23:59 +0000 | The end time in a day when TiDB can perform automatic update |
When the ratio of the number of modified rows to the total number of rows of tbl in a table is greater than tidb_auto_analyze_ratio, and the current time is between tidb_auto_analyze_start_time and tidb_auto_analyze_end_time, TiDB executes the ANALYZE TABLE tbl statement in the background to automatically update the statistics on this table.
To avoid the situation that modifying a small amount of data on a small table frequently triggers the automatic update, when a table has less than 1000 rows, such data modifying does not trigger the automatic update in TiDB. You can use the SHOW STATS_META statement to view the number of rows in a table.
Since TiDB v6.0, TiDB supports using the KILL statement to terminate an ANALYZE task running in the background. If you find that an ANALYZE task running in the background consumes a lot of resources and affects your application, you can terminate the ANALYZE task by taking the following steps:
- Execute the following SQL statement:
```sql
SHOW ANALYZE STATUS
```
By checking the `instance` column and the `process_id` column in the result, you can get the TiDB instance address and the task `ID` of the background `ANALYZE` task.
Terminate the
ANALYZEtask that is running in the background.- If
enable-global-killistrue(trueby default), you can execute theKILL TIDB ${id};statement directly, where${id}is theIDof the backgroundANALYZEtask obtained from the previous step. - If
enable-global-killisfalse, you need to use a client to connect to the TiDB instance that is executing the backendANALYZEtask, and then execute theKILL TIDB ${id};statement. If you use a client to connect to another TiDB instance, or if there is a proxy between the client and the TiDB cluster, theKILLstatement cannot terminate the backgroundANALYZEtask.
- If
For more information on the KILL statement, see KILL.
Control ANALYZE concurrency
When you run the ANALYZE statement, you can adjust the concurrency using the following parameters, to control its effect on the system.
tidb_build_stats_concurrency
Currently, when you run the ANALYZE statement, the task is divided into multiple small tasks. Each task only works on one column or index. You can use the tidb_build_stats_concurrency parameter to control the number of simultaneous tasks. The default value is 4.
tidb_distsql_scan_concurrency
When you analyze regular columns, you can use the tidb_distsql_scan_concurrency parameter to control the number of Region to be read at one time. The default value is 15.
tidb_index_serial_scan_concurrency
When you analyze index columns, you can use the tidb_index_serial_scan_concurrency parameter to control the number of Region to be read at one time. The default value is 1.
Persist ANALYZE configurations
Since v5.4.0, TiDB supports persisting some ANALYZE configurations. With this feature, the existing configurations can be easily reused for future statistics collection.
The following are the ANALYZE configurations that support persistence:
| Configurations | Corresponding ANALYZE syntax |
|---|---|
| The number of histogram buckets | WITH NUM BUCKETS |
| The number of Top-N | WITH NUM TOPN |
| The number of samples | WITH NUM SAMPLES |
| The sampling rate | WITH FLOATNUM SAMPLERATE |
The ANALYZE column type | AnalyzeColumnOption ::= ( 'ALL COLUMNS' | 'PREDICATE COLUMNS' | 'COLUMNS' ColumnNameList ) |
The ANALYZE column | ColumnNameList ::= Identifier ( ',' Identifier )* |
Enable ANALYZE configuration persistence
The ANALYZE configuration persistence feature is enabled by default (the system variable tidb_analyze_version is 2 and tidb_persist_analyze_options is ON by default).
You can use this feature to record the persistence configurations specified in the ANALYZE statement when executing the statement manually. Once recorded, the next time TiDB automatically updates statistics or you manually collect statistics without specifying these configuration, TiDB will collect statistics according to the recorded configurations.
When you manually execute the ANALYZE statement multiple times with persistence configurations specified, TiDB overwrites the previously recorded persistent configuration using the new configurations specified by the latest ANALYZE statement.
Disable ANALYZE configuration persistence
To disable the ANALYZE configuration persistence feature, set the tidb_persist_analyze_options system variable to OFF. Because the ANALYZE configuration persistence feature is not applicable to tidb_analyze_version = 1, setting tidb_analyze_version = 1 can also disable the feature.
After disabling the ANALYZE configuration persistence feature, TiDB does not clear the persisted configuration records. Therefore, if you enable this feature again, TiDB continues to collect statistics using the previously recorded persistent configurations.
The memory quota for collecting statistics
Since TiDB v6.1.0, you can use the system variable tidb_mem_quota_analyze to control the memory quota for collecting statistics in TiDB.
To set a proper value of tidb_mem_quota_analyze, consider the data size of the cluster. When the default sampling rate is used, the main considerations are the number of columns, the size of column values, and the memory configuration of TiDB. Consider the following suggestions when you configure the maximum and minimum values:
- Minimum value: should be greater than the maximum memory usage when TiDB collects statistics from the table with the most columns. An approximate reference: when TiDB collects statistics from a table with 20 columns using the default configuration, the maximum memory usage is about 800 MiB; when TiDB collects statistics from a table with 160 columns using the default configuration, the maximum memory usage is about 5 GiB.
- Maximum value: should be less than the available memory when TiDB is not collecting statistics.
View ANALYZE state
When executing the ANALYZE statement, you can view the current state of ANALYZE using the following SQL statement:
SHOW ANALYZE STATUS [ShowLikeOrWhere]
This statement returns the state of ANALYZE. You can use ShowLikeOrWhere to filter the information you need.
Currently, the SHOW ANALYZE STATUS statement returns the following 11 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| table_schema | The database name |
| table_name | The table name |
| partition_name | The partition name |
| job_info | The task information. If an index is analyzed, this information will include the index name. When tidb_analyze_version =2, this information will include configuration items such as sample rate. |
| processed_rows | The number of rows that have been analyzed |
| start_time | The time at which the task starts |
| state | The state of a task, including pending, running, finished, and failed |
| fail_reason | The reason why the task fails. If the execution is successful, the value is NULL. |
| instance | The TiDB instance that executes the task |
| process_id | The process ID that executes the task |
Starting from TiDB v6.1.0, the SHOW ANALYZE STATUS statement supports showing cluster-level tasks. Even after a TiDB restart, you can still view task records before the restart using this statement. Before TiDB v6.1.0, the SHOW ANALYZE STATUS statement can only show instance-level tasks, and task records are cleared after a TiDB restart.
SHOW ANALYZE STATUS shows the most recent task records only. Starting from TiDB v6.1.0, you can view the history tasks within the last 7 days through the system table mysql.analyze_jobs.
When tidb_mem_quota_analyze is set and an automatic ANALYZE task running in the TiDB background uses more memory than this threshold, the task will be retried. You can see failed and retried tasks in the output of the SHOW ANALYZE STATUS statement.
When tidb_max_auto_analyze_time is greater than 0 and an automatic ANALYZE task running in the TiDB background takes more time than this threshold, the task will be terminated.
mysql> SHOW ANALYZE STATUS [ShowLikeOrWhere];
+--------------+------------+----------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+----------------+---------------------+---------------------+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Table_schema | Table_name | Partition_name | Job_info | Processed_rows | Start_time | End_time | State | Fail_reason |
+--------------+------------+----------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+----------------+---------------------+---------------------+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| test | sbtest1 | | retry auto analyze table all columns with 100 topn, 0.055 samplerate | 2000000 | 2022-05-07 16:41:09 | 2022-05-07 16:41:20 | finished | NULL |
| test | sbtest1 | | auto analyze table all columns with 100 topn, 0.5 samplerate | 0 | 2022-05-07 16:40:50 | 2022-05-07 16:41:09 | failed | analyze panic due to memory quota exceeds, please try with smaller samplerate |
View statistics
You can view the statistics status using the following statements.
Metadata of tables
You can use the SHOW STATS_META statement to view the total number of rows and the number of updated rows.
SHOW STATS_META [ShowLikeOrWhere];
The syntax of ShowLikeOrWhereOpt is as follows:

Currently, the SHOW STATS_META statement returns the following 6 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The database name |
table_name | The table name |
partition_name | The partition name |
update_time | The time of the update |
modify_count | The number of modified rows |
row_count | The total number of rows |
Health state of tables
You can use the SHOW STATS_HEALTHY statement to check the health state of tables and roughly estimate the accuracy of the statistics. When modify_count >= row_count, the health state is 0; when modify_count < row_count, the health state is (1 - modify_count/row_count) * 100.
The syntax is as follows:
SHOW STATS_HEALTHY [ShowLikeOrWhere];
The synopsis of SHOW STATS_HEALTHY is:

Currently, the SHOW STATS_HEALTHY statement returns the following 4 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The database name |
table_name | The table name |
partition_name | The partition name |
healthy | The health state of tables |
Metadata of columns
You can use the SHOW STATS_HISTOGRAMS statement to view the number of different values and the number of NULL in all the columns.
Syntax as follows:
SHOW STATS_HISTOGRAMS [ShowLikeOrWhere]
This statement returns the number of different values and the number of NULL in all the columns. You can use ShowLikeOrWhere to filter the information you need.
Currently, the SHOW STATS_HISTOGRAMS statement returns the following 10 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The database name |
table_name | The table name |
partition_name | The partition name |
column_name | The column name (when is_index is 0) or the index name (when is_index is 1) |
is_index | Whether it is an index column or not |
update_time | The time of the update |
distinct_count | The number of different values |
null_count | The number of NULL |
avg_col_size | The average length of columns |
| correlation | The Pearson correlation coefficient of the column and the integer primary key, which indicates the degree of association between the two columns |
Buckets of histogram
You can use the SHOW STATS_BUCKETS statement to view each bucket of the histogram.
The syntax is as follows:
SHOW STATS_BUCKETS [ShowLikeOrWhere]
The diagram is as follows:

This statement returns information about all the buckets. You can use ShowLikeOrWhere to filter the information you need.
Currently, the SHOW STATS_BUCKETS statement returns the following 11 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The database name |
table_name | The table name |
partition_name | The partition name |
column_name | The column name (when is_index is 0) or the index name (when is_index is 1) |
is_index | Whether it is an index column or not |
bucket_id | The ID of a bucket |
count | The number of all the values that falls on the bucket and the previous buckets |
repeats | The occurrence number of the maximum value |
lower_bound | The minimum value |
upper_bound | The maximum value |
ndv | The number of different values in the bucket. When tidb_analyze_version = 1, ndv is always 0, which has no actual meaning. |
Top-N information
You can use the SHOW STATS_TOPN statement to view the Top-N information currently collected by TiDB.
The syntax is as follows:
SHOW STATS_TOPN [ShowLikeOrWhere];
Currently, the SHOW STATS_TOPN statement returns the following 7 columns:
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The database name |
table_name | The table name |
partition_name | The partition name |
column_name | The column name (when is_index is 0) or the index name (when is_index is 1) |
is_index | Whether it is an index column or not |
value | The value of this column |
count | How many times the value appears |
Delete statistics
You can run the DROP STATS statement to delete statistics.
DROP STATS TableName
The preceding statement deletes all statistics of TableName. If a partitioned table is specified, this statement will delete statistics of all partitions in this table as well as GlobalStats generated in dynamic pruning mode.
DROP STATS TableName PARTITION PartitionNameList;
This preceding statement only deletes statistics of the specified partitions in PartitionNameList.
DROP STATS TableName GLOBAL;
The preceding statement only deletes GlobalStats generated in dynamic pruning mode of the specified table.
Load statistics
By default, depending on the size of column statistics, TiDB loads statistics differently as follows:
- For statistics that consume small amounts of memory (such as count, distinctCount, and nullCount), as long as the column data is updated, TiDB automatically loads the corresponding statistics into memory for use in the SQL optimization stage.
- For statistics that consume large amounts of memory (such as histograms, TopN, and Count-Min Sketch), to ensure the performance of SQL execution, TiDB loads the statistics asynchronously on demand. Take histograms as an example. TiDB loads histogram statistics on a column into memory only when the optimizer uses the histogram statistics on that column. On-demand asynchronous statistics loading does not affect the performance of SQL execution but might provide incomplete statistics for SQL optimization.
Since v5.4.0, TiDB introduces the synchronously loading statistics feature. This feature allows TiDB to synchronously load large-sized statistics (such as histograms, TopN, and Count-Min Sketch statistics) into memory when you execute SQL statements, which improves the completeness of statistics for SQL optimization.
To enable this feature, set the value of the tidb_stats_load_sync_wait system variable to a timeout (in milliseconds) that SQL optimization can wait for at most to synchronously load complete column statistics. The default value of this variable is 100, indicating that the feature is enabled.
After enabling the synchronously loading statistics feature, you can further configure the feature as follows:
- To control how TiDB behaves when the waiting time of SQL optimization reaches the timeout, modify the value of the
tidb_stats_load_pseudo_timeoutsystem variable. The default value of this variable isON, indicating that after the timeout, the SQL optimization process does not use any histogram, TopN, or CMSketch statistics on any columns. If this variable is set toOFF, after the timeout, SQL execution fails. - To specify the maximum number of columns that the synchronously loading statistics feature can process concurrently, modify the value of the
stats-load-concurrencyoption in the TiDB configuration file. The default value is5. - To specify the maximum number of column requests that the synchronously loading statistics feature can cache, modify the value of the
stats-load-queue-sizeoption in the TiDB configuration file. The default value is1000.
Import and export statistics
Export statistics
The interface to export statistics is as follows:
- To obtain the JSON format statistics of the
${table_name}table in the${db_name}database:
```
http://${tidb-server-ip}:${tidb-server-status-port}/stats/dump/${db_name}/${table_name}
```
For example:
```
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:10080/stats/dump/test/t1 -o /tmp/t1.json
```
- To obtain the JSON format statistics of the
${table_name}table in the${db_name}database at specific time:
```
http://${tidb-server-ip}:${tidb-server-status-port}/stats/dump/${db_name}/${table_name}/${yyyyMMddHHmmss}
```
Import statistics
Generally, the imported statistics refer to the JSON file obtained using the export interface.
Syntax:
LOAD STATS 'file_name'
file_name is the file name of the statistics to be imported.
Lock statistics
Since v6.5.0, TiDB supports locking statistics. After the statistics of a table are locked, the statistics of the table cannot be modified and the ANALYZE statement cannot be executed on the table. For example:
Create table t, and insert data into it. When the statistics of table t are not locked, the ANALYZE statement can be successfully executed.
mysql> create table t(a int, b int);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> insert into t values (1,2), (3,4), (5,6), (7,8);
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> analyze table t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.02 sec)
mysql> show warnings;
+-------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+-------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| Note | 1105 | Analyze use auto adjusted sample rate 1.000000 for table test.t |
+-------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Lock the statistics of table t and execute ANALYZE. From the output of SHOW STATS_LOCKED, you can see that the statistics of table t have been locked. The warning message shows that the ANALYZE statement has skipped table t.
mysql> lock stats t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show stats_locked;
+---------+------------+----------------+--------+
| Db_name | Table_name | Partition_name | Status |
+---------+------------+----------------+--------+
| test | t | | locked |
+---------+------------+----------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> analyze table t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings;
+---------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+---------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| Note | 1105 | Analyze use auto adjusted sample rate 1.000000 for table test.t |
| Warning | 1105 | skip analyze locked table: t |
+---------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Unlock the statistics of table t and ANALYZE can be successfully executed again.
mysql> unlock stats t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> analyze table t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.03 sec)
mysql> show warnings;
+-------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+-------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| Note | 1105 | Analyze use auto adjusted sample rate 1.000000 for table test.t |
+-------+------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)