TiCDC Overview
TiCDC is a tool used for replicating incremental data of TiDB. Specifically, TiCDC pulls TiKV change logs, sorts captured data, and exports row-based incremental data to downstream databases.
Usage scenarios
- Database disaster recovery: TiCDC can be used for disaster recovery between homogeneous databases to ensure eventual data consistency of primary and secondary databases after a disaster event. This function works only with TiDB primary and secondary clusters.
- Data integration: TiCDC provides TiCDC Canal-JSON Protocol, which allows other systems to subscribe data changes from TiCDC. In this way, TiCDC provides data sources for various scenarios such as monitoring, caching, global indexing, data analysis, and primary-secondary replication between heterogeneous databases.
TiCDC architecture
When TiCDC is running, it is a stateless node that achieves high availability through etcd in PD. The TiCDC cluster supports creating multiple replication tasks to replicate data to multiple different downstream platforms.
The architecture of TiCDC is shown in the following figure:
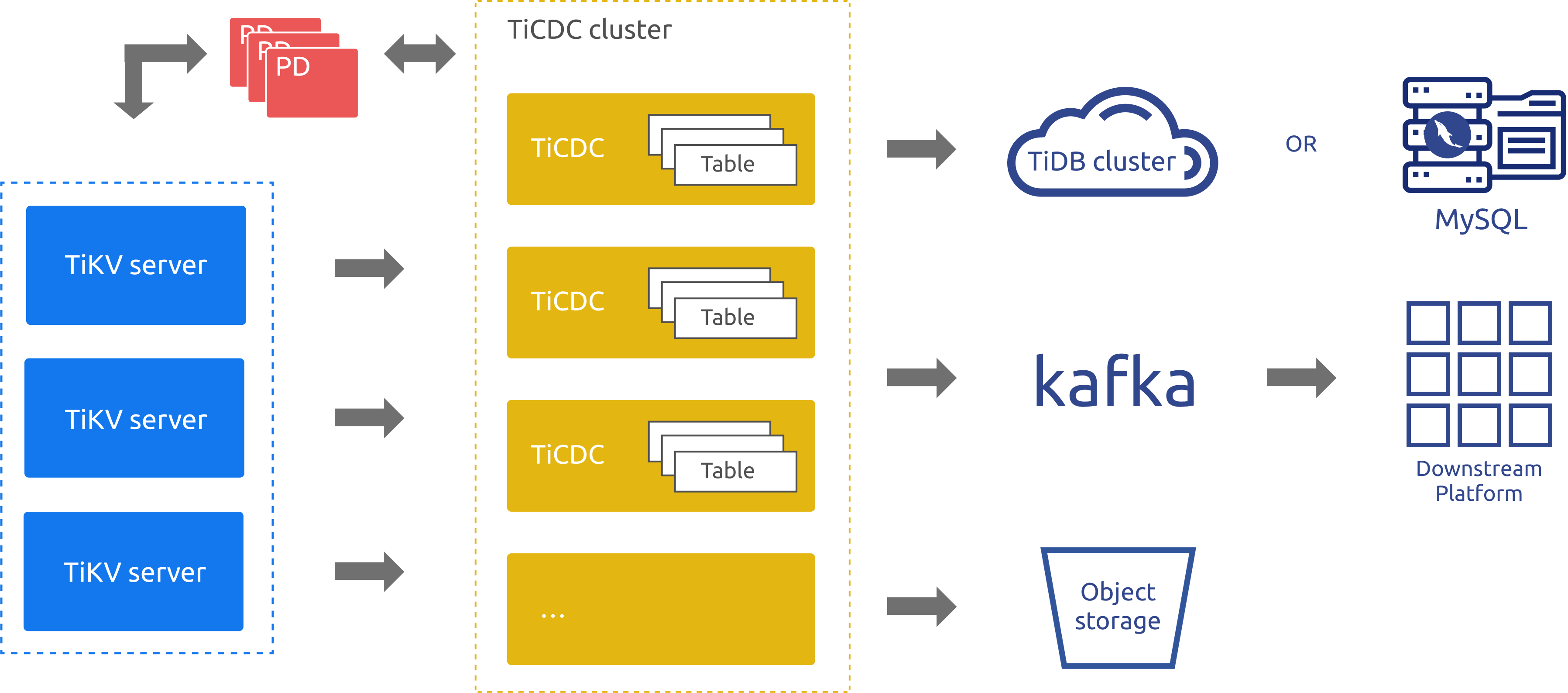
System roles
TiKV CDC component: Only outputs key-value (KV) change logs.
- Assembles KV change logs in the internal logic.
- Provides the interface to output KV change logs. The data sent includes real-time change logs and incremental scan change logs.
capture: The operating process of TiCDC. Multiplecapturesform a TiCDC cluster that replicates KV change logs.- Each
capturepulls a part of KV change logs. - Sorts the pulled KV change log(s).
- Restores the transaction to downstream or outputs the log based on the TiCDC open protocol.
- Each
Replication features
This section introduces the replication features of TiCDC.
Sink support
Currently, the TiCDC sink component supports replicating data to the following downstream platforms:
- Databases compatible with MySQL protocol. The sink component provides the final consistency support.
- Kafka based on the TiCDC Open Protocol. The sink component ensures the row-level order, final consistency or strict transactional consistency.
Ensure replication order and consistency
Replication order
For all DDL or DML statements, TiCDC outputs them at least once.
When the TiKV or TiCDC cluster encounters failure, TiCDC might send the same DDL/DML statement repeatedly. For duplicated DDL/DML statements:
- MySQL sink can execute DDL statements repeatedly. For DDL statements that can be executed repeatedly in the downstream, such as
truncate table, the statement is executed successfully. For those that cannot be executed repeatedly, such ascreate table, the execution fails, and TiCDC ignores the error and continues the replication. - Kafka sink sends messages repeatedly, but the duplicate messages do not affect the constraints of
Resolved Ts. Users can filter the duplicated messages from Kafka consumers.
- MySQL sink can execute DDL statements repeatedly. For DDL statements that can be executed repeatedly in the downstream, such as
Replication consistency
MySQL sink
TiCDC does not split single-table transactions and ensures the atomicity of single-table transactions.
TiCDC does not ensure that the execution order of downstream transactions is the same as that of upstream transactions.
TiCDC splits cross-table transactions in the unit of table and does not ensure the atomicity of cross-table transactions.
TiCDC ensures that the order of single-row updates is consistent with that in the upstream.
Kafka sink
- TiCDC provides different strategies for data distribution. You can distribute data to different Kafka partitions based on the table, primary key, or timestamp.
- For different distribution strategies, the different consumer implementations can achieve different levels of consistency, including row-level consistency, eventual consistency, or cross-table transactional consistency.
- TiCDC does not have an implementation of Kafka consumers, but only provides TiCDC Open Protocol. You can implement the Kafka consumer according to this protocol.
Restrictions
There are some restrictions when using TiCDC.
Requirements for valid index
TiCDC only replicates the table that has at least one valid index. A valid index is defined as follows:
- The primary key (
PRIMARY KEY) is a valid index. - The unique index (
UNIQUE INDEX) that meets the following conditions at the same time is a valid index:- Every column of the index is explicitly defined as non-nullable (
NOT NULL). - The index does not have the virtual generated column (
VIRTUAL GENERATED COLUMNS).
- Every column of the index is explicitly defined as non-nullable (
Since v4.0.8, TiCDC supports replicating tables without a valid index by modifying the task configuration. However, this compromises the guarantee of data consistency to some extent. For more details, see Replicate tables without a valid index.
Unsupported scenarios
Currently, the following scenarios are not supported:
- The TiKV cluster that uses RawKV alone.
- The DDL operation
CREATE SEQUENCEand the SEQUENCE function in TiDB. When the upstream TiDB usesSEQUENCE, TiCDC ignoresSEQUENCEDDL operations/functions performed upstream. However, DML operations usingSEQUENCEfunctions can be correctly replicated.
TiCDC only provides partial support for scenarios of large transactions in the upstream. For details, refer to FAQ: Does TiCDC support replicating large transactions? Is there any risk?.
Install and deploy TiCDC
You can either deploy TiCDC along with a new TiDB cluster or add the TiCDC component to an existing TiDB cluster. For details, see Deploy TiCDC.
Manage TiCDC Cluster and Replication Tasks
Currently, you can use the cdc cli tool to manage the status of a TiCDC cluster and data replication tasks. For details, see:
- Use
cdc clito manage cluster status and data replication task - Use OpenAPI to manage cluster status and data replication task
TiCDC Open Protocol
TiCDC Open Protocol is a row-level data change notification protocol that provides data sources for monitoring, caching, full-text indexing, analysis engines, and primary-secondary replication between different databases. TiCDC complies with TiCDC Open Protocol and replicates data changes of TiDB to third-party data medium such as MQ (Message Queue). For more information, see TiCDC Open Protocol.
Compatibility notes
Incompatibility issue caused by using the TiCDC v5.0.0-rc cdc cli tool to operate a v4.0.x cluster
When using the cdc cli tool of TiCDC v5.0.0-rc to operate a v4.0.x TiCDC cluster, you might encounter the following abnormal situations:
If the TiCDC cluster is v4.0.8 or an earlier version, using the v5.0.0-rc
cdc clitool to create a replication task might cause cluster anomalies and get the replication task stuck.If the TiCDC cluster is v4.0.9 or a later version, using the v5.0.0-rc
cdc clitool to create a replication task will cause the old value and unified sorter features to be unexpectedly enabled by default.
Solutions: Use the cdc executable file corresponding to the TiCDC cluster version to perform the following operations:
- Delete the changefeed created using the v5.0.0-rc
cdc clitool. For example, run thetiup cdc:v4.0.9 cli changefeed remove -c xxxx --pd=xxxxx --forcecommand. - If the replication task is stuck, restart the TiCDC cluster. For example, run the
tiup cluster restart <cluster_name> -R cdccommand. - Re-create the changefeed. For example, run the
tiup cdc:v4.0.9 cli changefeed create --sink-uri=xxxx --pd=xxxcommand.
Compatibility notes for sort-dir and data-dir
The sort-dir configuration is used to specify the temporary file directory for the TiCDC sorter. Its functionalities might vary in different versions. The following table lists sort-dir's compatibility changes across versions.
| Version | sort-engine functionality | Note | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| v4.0.11 or an earlier v4.0 version, v5.0.0-rc | It is a changefeed configuration item and specifies temporary file directory for the file sorter and unified sorter. | In these versions, file sorter and unified sorter are experimental features and NOT recommended for the production environment. If multiple changefeeds use the unified sorter as its sort-engine, the actual temporary file directory might be the sort-dir configuration of any changefeed, and the directory used for each TiCDC node might be different. | It is not recommended to use unified sorter in the production environment. |
| v4.0.12, v4.0.13, v5.0.0, and v5.0.1 | It is a configuration item of changefeed or of cdc server. | By default, the sort-dir configuration of a changefeed does not take effect, and the sort-dir configuration of cdc server defaults to /tmp/cdc_sort. It is recommended to only configure cdc server in the production environment.If you use TiUP to deploy TiCDC, it is recommended to use the latest TiUP version and set sorter.sort-dir in the TiCDC server configuration.The unified sorter is enabled by default in v4.0.13, v5.0.0, and v5.0.1. If you want to upgrade your cluster to these versions, make sure that you have correctly configured sorter.sort-dir in the TiCDC server configuration. | You need to configure sort-dir using the cdc server command-line parameter (or TiUP). |
| v4.0.14 and later v4.0 versions, v5.0.3 and later v5.0 versions, later TiDB versions | sort-dir is deprecated. It is recommended to configure data-dir. | You can configure data-dir using the latest version of TiUP. In these TiDB versions, unified sorter is enabled by default. Make sure that data-dir has been configured correctly when you upgrade your cluster. Otherwise, /tmp/cdc_data will be used by default as the temporary file directory. If the storage capacity of the device where the directory is located is insufficient, the problem of insufficient hard disk space might occur. In this situation, the previous sort-dir configuration of changefeed will become invalid. | You need to configure data-dir using the cdc server command-line parameter (or TiUP). |
Compatibility with temporary tables
Since v5.3.0, TiCDC supports global temporary tables. Replicating global temporary tables to the downstream using TiCDC of a version earlier than v5.3.0 causes table definition error.
If the upstream cluster contains a global temporary table, the downstream TiDB cluster is expected to be v5.3.0 or a later version. Otherwise, an error occurs during the replication process.
TiCDC FAQs and troubleshooting
- To learn the FAQs of TiCDC, see TiCDC FAQs.
- To learn how to troubleshoot TiCDC, see Troubleshoot TiCDC.