EXPLAIN ANALYZE
The EXPLAIN ANALYZE statement works similar to EXPLAIN, with the major difference being that it will actually execute the statement. This allows you to compare the estimates used as part of query planning to actual values encountered during execution. If the estimates differ significantly from the actual values, you should consider running ANALYZE TABLE on the affected tables.
Synopsis
ExplainSym:
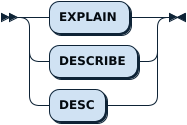
ExplainStmt:
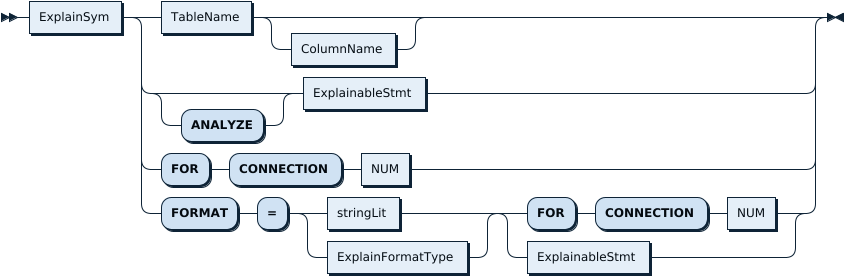
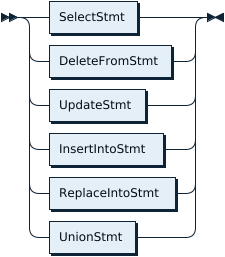
ExplainableStmt:
Examples
mysql> CREATE TABLE t1 (id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, c1 INT NOT NULL);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO t1 (c1) VALUES (1), (2), (3);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE id = 1;
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+---------------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info | execution info |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+---------------------------+
| Point_Get_1 | 1.00 | root | table:t1, handle:1 | time:0ns, loops:0, rows:0 |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+---------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM t1;
+-------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info | execution info |
+-------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------+
| TableReader_5 | 10000.00 | root | data:TableScan_4 | time:931.759µs, loops:2, rows:3 |
| └─TableScan_4 | 10000.00 | cop | table:t1, range:[-inf,+inf], keep order:false, stats:pseudo | time:0s, loops:0, rows:3 |
+-------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL compatibility
EXPLAIN ANALYZE is a feature of MySQL 8.0, but both the output format and the potential execution plans in TiDB differ substantially from MySQL.