BR Tool Overview
BR (Backup & Restore) is a command-line tool for distributed backup and restoration of the TiDB cluster data. It is supported to use BR only in TiDB v3.1 and later versions.
Compared with dumpling and mydumper/loader, BR is more suitable for scenarios of huge data volume.
This document describes BR's implementation principles, recommended deployment configuration, usage restrictions, several methods to use BR, etc.
Implementation principles
BR sends the backup or restoration commands to each TiKV node. After receiving these commands, TiKV performs the corresponding backup or restoration operations.
Each TiKV node has a path in which the backup files generated in the backup operation are stored and from which the stored backup files are read during the restoration.
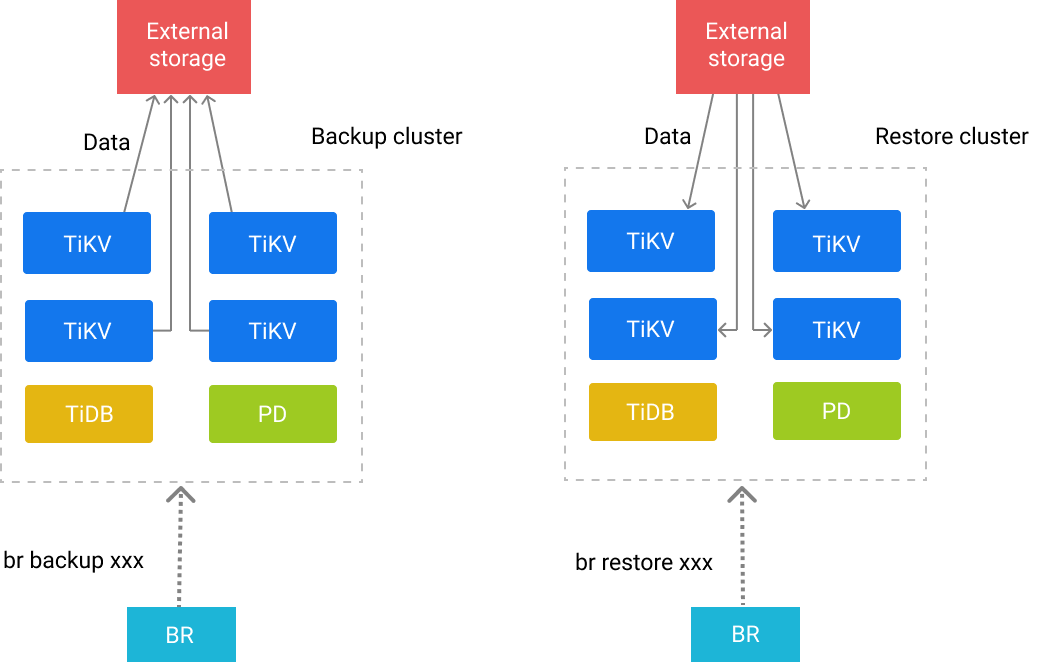
Backup principle
When BR performs a backup operation, it first obtains the following information from PD:
- The current TS (timestamp) as the time of the backup snapshot
- The TiKV node information of the current cluster
According to these information, BR starts a TiDB instance internally to obtain the database or table information corresponding to the TS, and filters out the system databases (information_schema, performance_schema, mysql) at the same time.
According to the backup sub-command, BR adopts the following two types of backup logic:
- Full backup: BR traverses all the tables and constructs the KV range to be backed up according to each table.
- Single table backup: BR constructs the KV range to be backed up according a single table.
Finally, BR collects the KV range to be backed up and sends the complete backup request to the TiKV node of the cluster.
The structure of the request:
BackupRequest{
ClusterId, // The cluster ID.
StartKey, // The starting key of the backup (backed up).
EndKey, // The ending key of the backup (not backed up).
StartVersion, // The version of the last backup snapshot, used for the incremental backup.
EndVersion, // The backup snapshot time.
StorageBackend, // The path where backup files are stored.
RateLimit, // Backup speed (MB/s).
}
After receiving the backup request, the TiKV node traverses all Region leaders on the node to find the Regions that overlap with the KV ranges in this request. The TiKV node backs up some or all of the data within the range, and generates the corresponding SST file.
After finishing backing up the data of the corresponding Region, the TiKV node returns the metadata to BR. BR collects the metadata and stores it in the backupmeta file which is used for restoration.
If StartVersion is not 0, the backup is seen as an incremental backup. In addition to KVs, BR also collects DDLs between [StartVersion, EndVersion). During data restoration, these DDLs are restored first.
If checksum is enabled when you execute the backup command, BR calculates the checksum of each backed up table for data check.
Types of backup files
Two types of backup files are generated in the path where backup files are stored:
- The SST file: stores the data that the TiKV node backed up.
- The
backupmetafile: stores the metadata of this backup operation, including the number, the key range, the size, and the Hash (sha256) value of the backup files.
The format of the SST file name
The SST file is named in the format of storeID_regionID_regionEpoch_keyHash_cf, where
storeIDis the TiKV node ID;regionIDis the Region ID;regionEpochis the version number of the Region;keyHashis the Hash (sha256) value of the startKey of a range, which ensures the uniqueness of a key;cfindicates the Column Family of RocksDB (defaultorwriteby default).
Restoration principle
During the data restoration process, BR performs the following tasks in order:
It parses the
backupmetafile in the backup path, and then starts a TiDB instance internally to create the corresponding databases and tables based on the parsed information.It aggregates the parsed SST files according to the tables.
It pre-splits Regions according to the key range of the SST file so that every Region corresponds to at least one SST file.
It traverses each table to be restored and the SST file corresponding to each tables.
It finds the Region corresponding to the SST file and sends a request to the corresponding TiKV node for downloading the file. Then it sends a request for loading the file after the file is successfully downloaded.
After TiKV receives the request to load the SST file, TiKV uses the Raft mechanism to ensure the strong consistency of the SST data. After the downloaded SST file is loaded successfully, the file is deleted asynchronously.
After the restoration operation is completed, BR performs a checksum calculation on the restored data to compare the stored data with the backed up data.
Deploy and use BR
Recommended deployment configuration
- It is recommended that you deploy BR on the PD node.
- It is recommended that you mount a high-performance SSD to BR nodes and all TiKV nodes. A 10-gigabit network card is recommended. Otherwise, bandwidth is likely to be the performance bottleneck during the backup and restore process.
Usage restrictions
The following are the limitations of using BR for backup and restoration:
- It is supported to use BR only in TiDB v3.1 and later versions.
- When BR restores data to the upstream cluster of Drainer, Drainer cannot replicate the restored data to the downstream.
- In v3.1, you can perform restoration only on new clusters.
Best practices
The following are some recommended operations for using BR for backup and restoration:
- It is recommended that you perform the backup operation during off-peak hours to minimize the impact on applications.
- BR supports restore on clusters of different topologies. However, the online applications will be greatly impacted during the restore operation. It is recommended that you perform restore during the off-peak hours or use
rate-limitto limit the rate. - It is recommended that you execute multiple backup operations serially. Running different backup operations in parallel reduces backup performance and also affects the online application.
- It is recommended that you execute multiple restore operations serially. Running different restore operations in parallel increases Region conflicts and also reduces restore performance.
- It is recommended that you mount a shared storage (for example, NFS) on the backup path specified by
-s, to make it easier to collect and manage backup files. - It is recommended that you use a storage hardware with high throughput, because the throughput of a storage hardware limits the backup and restoration speed.
How to use BR
In TiDB versions above v3.1, you can run the BR tool using the command-line tool.
First, you need to download the binary file of the BR tool. See download link.
For how to use the command-line tool to perform backup and restore operations, see Use the BR command-line tool.