TiDB Architecture
The TiDB platform is comprised of three key components: the TiDB server, the PD server, and the TiKV server. In addition, TiDB also provides the TiSpark component for complex OLAP requirements.
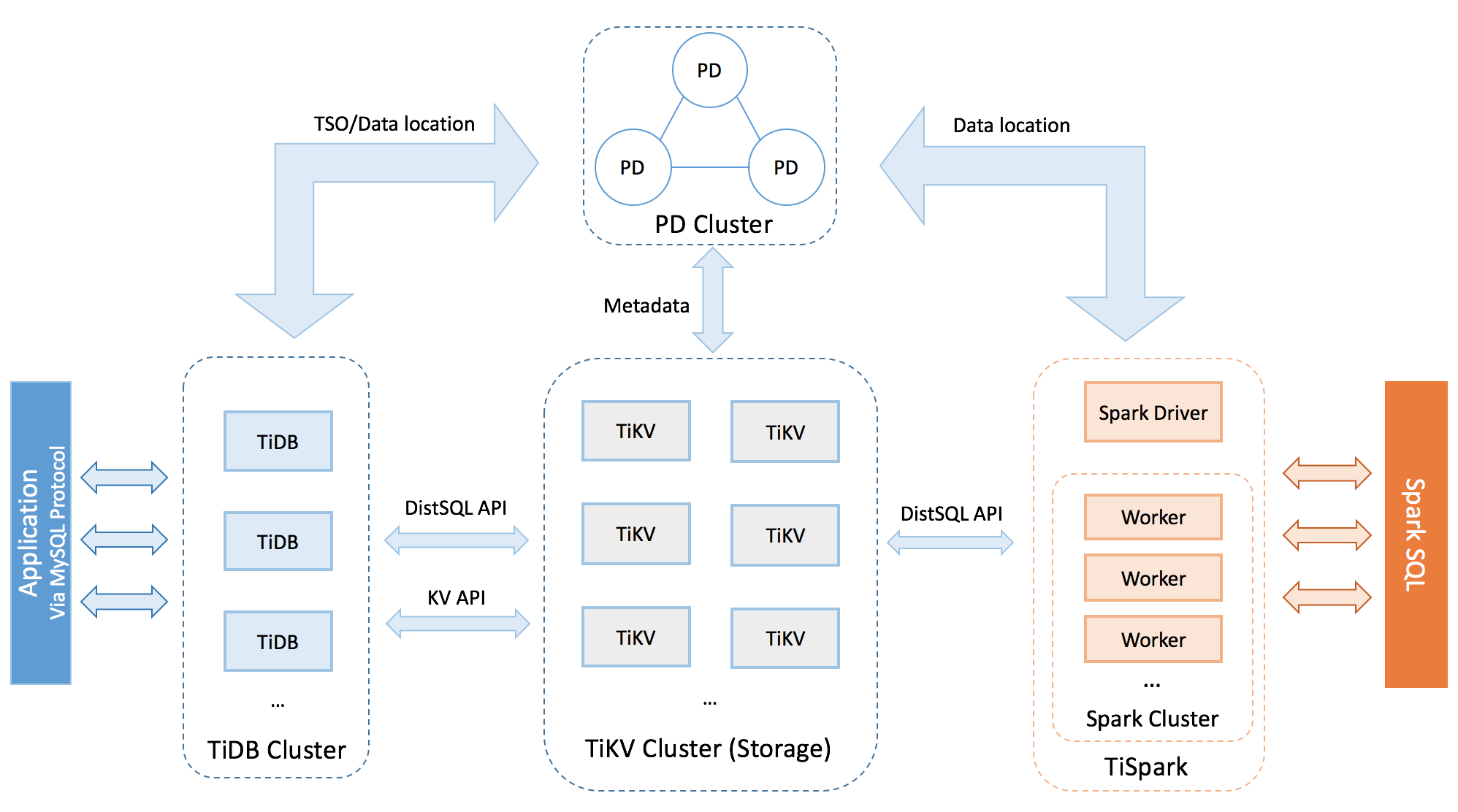
TiDB server
The TiDB server is in charge of the following operations:
Receiving the SQL requests
Processing the SQL related logics
Locating the TiKV address for storing and computing data through Placement Driver (PD)
Exchanging data with TiKV
Returning the result
The TiDB server is stateless. It does not store data and it is for computing only. TiDB is horizontally scalable and provides the unified interface to the outside through the load balancing components such as Linux Virtual Server (LVS), HAProxy, or F5.
Placement Driver server
The Placement Driver (PD) server is the managing component of the entire cluster and is in charge of the following three operations:
Storing the metadata of the cluster such as the region location of a specific key.
Scheduling and load balancing regions in the TiKV cluster, including but not limited to data migration and Raft group leader transfer.
Allocating the transaction ID that is globally unique and monotonically increasing.
The PD server ensures redundancy by using the Raft consensus algorithm. The Raft leader is responsible for handling all operations, with remaining PD servers available for high availability only. It is recommended to deploy PD as an odd number of nodes.
TiKV server
The TiKV server is responsible for storing data. From an external view, TiKV is a distributed transactional Key-Value storage engine. Region is the basic unit to store data. Each Region stores the data for a particular Key Range which is a left-closed and right-open interval from StartKey to EndKey. There are multiple Regions in each TiKV node. TiKV uses the Raft protocol for replication to ensure the data consistency and disaster recovery. The replicas of the same Region on different nodes compose a Raft Group. The load balancing of the data among different TiKV nodes is carried out by PD through scheduling the load in units of Region.
TiSpark
TiSpark deals with the complex OLAP requirements. TiSpark makes Spark SQL directly run on the storage layer of the TiDB cluster, combines the advantages of the distributed TiKV cluster, and integrates into the big data ecosystem. With TiSpark, TiDB can support both OLTP and OLAP scenarios in one cluster, so the users never need to worry about data replication.